Bearing steel is the steel used to manufacture ball bearings, rollers, and bearing rings. Bearing steel has high and uniform hardness and wear resistance, as well as high elastic limit. The requirements for the uniformity of chemical composition, content and distribution of non-metallic inclusions, and distribution of carbides in bearing steel are very strict, making it one of the most demanding steel grades in all steel production.
In 1976, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) included some common bearing steel grades in international standards, dividing bearing steel into four categories: fully quenched bearing steel, surface hardened bearing steel, stainless bearing steel, and high-temperature bearing steel, totaling 17 steel grades.
Bearing steel, also known as high carbon chromium steel, has a carbon content of about 1% Wc and a chromium content of 0.5% -1.65% Wcr. Bearing steel is divided into six categories: high carbon chromium bearing steel, chromium free bearing steel, carburized bearing steel, stainless bearing steel, medium high temperature bearing steel, and anti magnetic bearing steel.

High carbon chromium bearing steel GCr15 is the most widely produced bearing steel in the world, with a carbon content of about 1% (Wc) and a chromium content of about 1.5% (WCr). Since its birth in 1901, its main components have remained basically unchanged for more than 100 years. With the advancement of science and technology, research work continues and product quality continues to improve, accounting for more than 80% of the world's total bearing steel production. So much so that bearing steel, unless otherwise specified, refers to GCr15.
The advantages of chromium steel and stainless steel as bearing materials have been found to have anti rust effects. Moreover, chromium steel is a common bearing material. It is harder than stainless steel, so it can last longer. However, at higher temperatures, its performance deteriorates.
At a high temperature of 120 ℃, the bearing undergoes significant deformation and the load decreases. It can withstand high temperatures of 150 ℃, but an instantaneous temperature of 150 ℃ or higher will reduce the service life of the bearing. Heat treatment can make the bearing withstand a high temperature of 170 ℃.
The more common stainless steel 440 is used for bearings. It is hard enough and has strong load capacity (20% lower than brass steel), but it can prevent rust and withstand instantaneous high temperatures of 250 ℃ and continuous high temperatures of 300 ℃. We often mistakenly believe that all stainless steel is non-magnetic. 440 stainless steel is magnetic. It is not completely rust proof, but it is affected by salt, acid, and alkali.
316 grade has good rust resistance, non-magnetic, but softer, so the load is smaller. Because it is not sturdy, the 316 bearings are ineffective and feel rough.
Bearing steel is a type of steel used to manufacture rolling bearings such as balls, rollers, and sleeves. It can also be used to make precision measuring tools, cold stamping dies, machine tool screws, such as stamping dies, measuring tools, taps, and precision parts for diesel engine oil pumps. Bearing steel is the steel used to manufacture ball bearings, rollers, and bearing rings.
In order to meet the performance requirements for dynamic bearings mentioned above, the following basic performance requirements have been proposed for bearing steel materials:
(1) High contact fatigue strength,
(2) After heat treatment, it should have high hardness or a hardness that meets the performance requirements for bearing use,
(3) High wear resistance, low friction coefficient,
(4) High elastic limit,
(5) Good impact toughness and fracture toughness,
(6) Good dimensional stability,
(7) Good rust prevention performance,
(8) Good cold and hot processing performance.
Comparison of Bearing Material Performance
High carbon chromium bearing steel (GCr15/GCr15SMn/GCr18M0)
High carbon chromium bearing steel is a high carbon alloy steel containing 1.30-1.65% chromium. Its characteristics include a relatively uniform and stable microstructure after heat treatment, high and uniform hardness, good wear resistance, high contact fatigue strength, good dimensional stability, and corrosion resistance. After spheroidization annealing, its cutting performance is good. This type of steel can meet the requirements for bearings operating under general working conditions.
High carbon chromium bearing steel is widely used worldwide, with the commonly used grades being GCr15 and GCr15SiMn, which account for over 80% of the total bearing steel in China. These two types of steel have similar properties, but GCr15SiMn steel has better hardenability than GCr15 steel. Therefore, for larger bearing parts, GCr15SiMn steel is recommended.
GCr15 bearing steel is widely used in the manufacture of engine bearings for automobiles, tractors, tanks, airplanes, etc., as well as spindle bearings for machine tools, motors, and bearings for railway vehicles, mining machinery, and general machinery.
GCr15SiMn bearing steel is mainly used to manufacture bearings with large wall thickness, such as various large and extra large bearings, and is often used in heavy-duty machine tools and rolling mills under working conditions without significant impact loads.
Due to the high crack sensitivity and poor impact toughness of GCr15SiMn steel, it cannot fully meet the requirements for thick walled bearings with impact loads. The Ministry of Railways first proposed that the use of GCr15SiMn steel is not allowed for passenger car bearings. In addition, GCr15SiMn steel is also restricted for rolling mills and mining bearings with large wall thickness under high impact load conditions. GCr18Mo high hardenability steel and wear resistance have been developed. Its performance is superior to GCr15SiMn steel, and it can replace GCr15SiMn steel in railway bearings, rolling mill bearings, and mining machinery bearings.
Carbonized bearing steel (G20Cr2Ni4A)
G20Cr2Ni4A bearing steel is a high-quality alloy carburizing steel (low-carbon C: 0.17-0.23) used for manufacturing bearing parts. Bearing parts made of this type of steel have high hardness (hardness>HRC60), certain wear resistance, and high contact fatigue strength on the surface after heat treatment processes such as carburizing, quenching, and tempering. Low carbon C: 0.17-0.23 ensures good toughness at the core (hardness>HRC33-48). This surface hardened core has the characteristic of toughness, making carburized bearing steel particularly suitable for stable operation under high impact load conditions. In summary, the advantages of carburizing steel bearings are:
(1) After carburizing and quenching, the surface retains the compressive stress state and has good fatigue strength.
(2) Strong ability to withstand impact loads, and the surface hardening layer has microcracks that are not easily propagated inward. The surface has higher hardness while the core hardness is lower (generally 35HRC~40HRC), and compared with high carbon chromium bearing steel, it has better core impact toughness.
(3) The depth and concentration of carburizing can be adjusted as needed.
(4) Not limited by the size and wall thickness of bearing components.
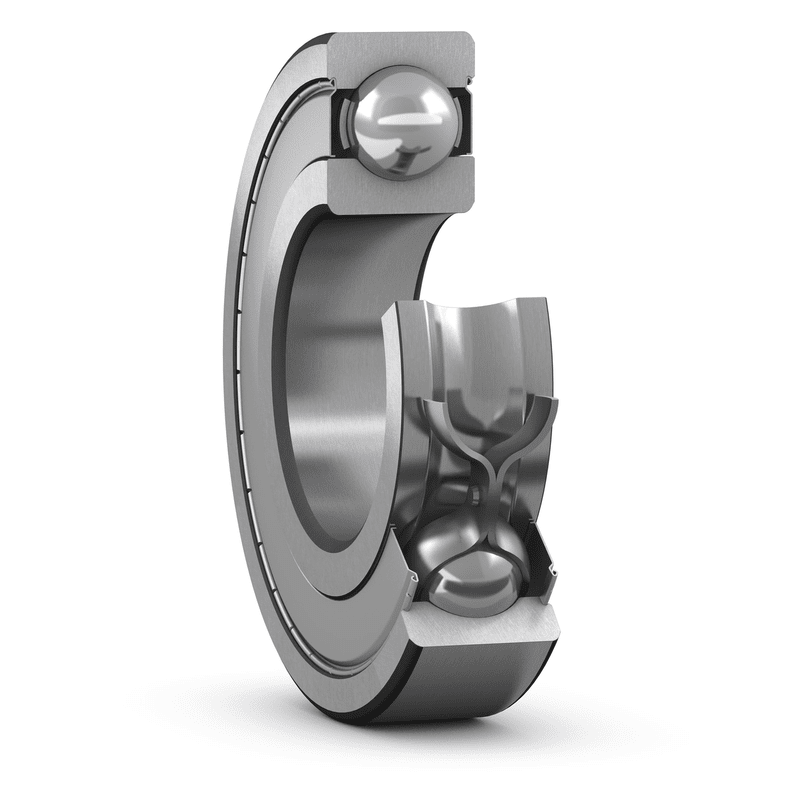

Single row deep groove ball bearings are the most widely used type of bearing. Provide closed (with sealed or dust cover) or open design. Open type be...
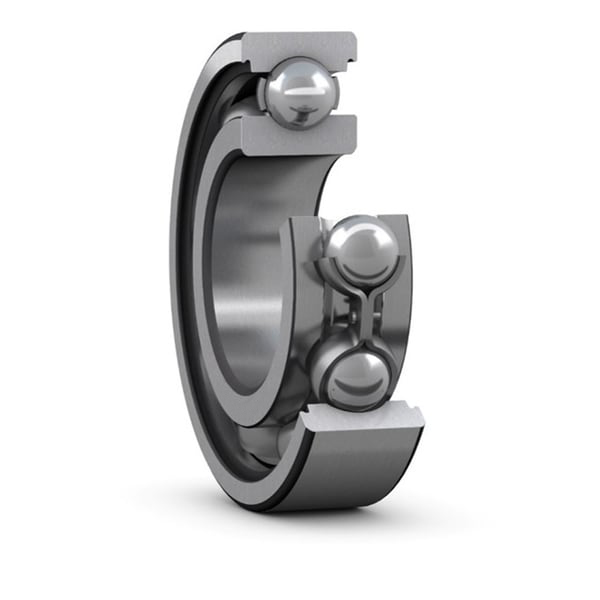

Stainless steel deep groove ball bearings can resist corrosion caused by moisture and other media. Provide closed (with sealed or dust cover) or open ...
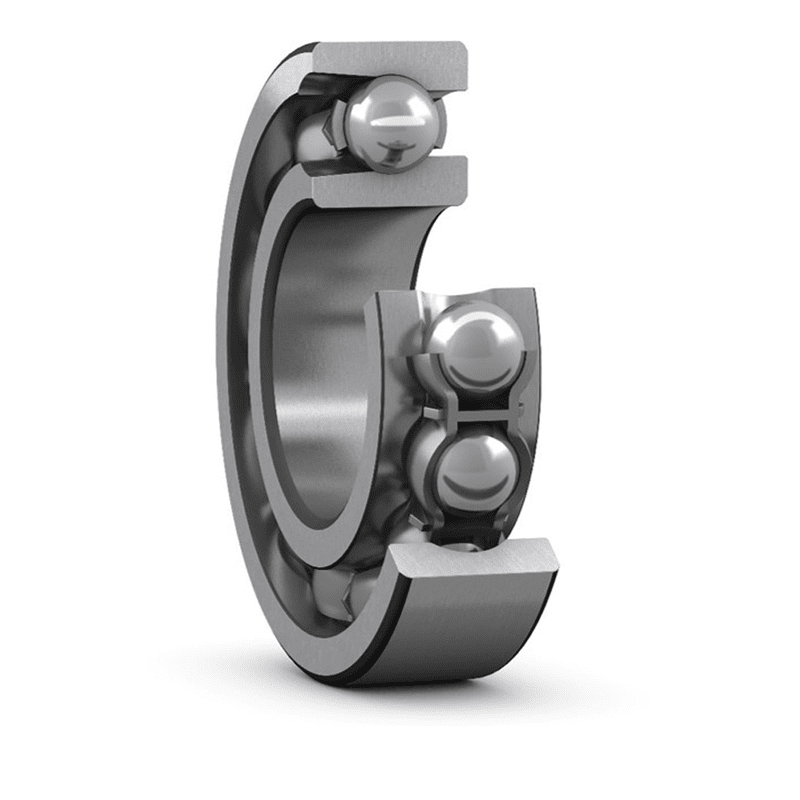

A single row deep groove ball bearing with a ball loading notch has a ball loading notch on both the inner and outer rings, which is used to load more...
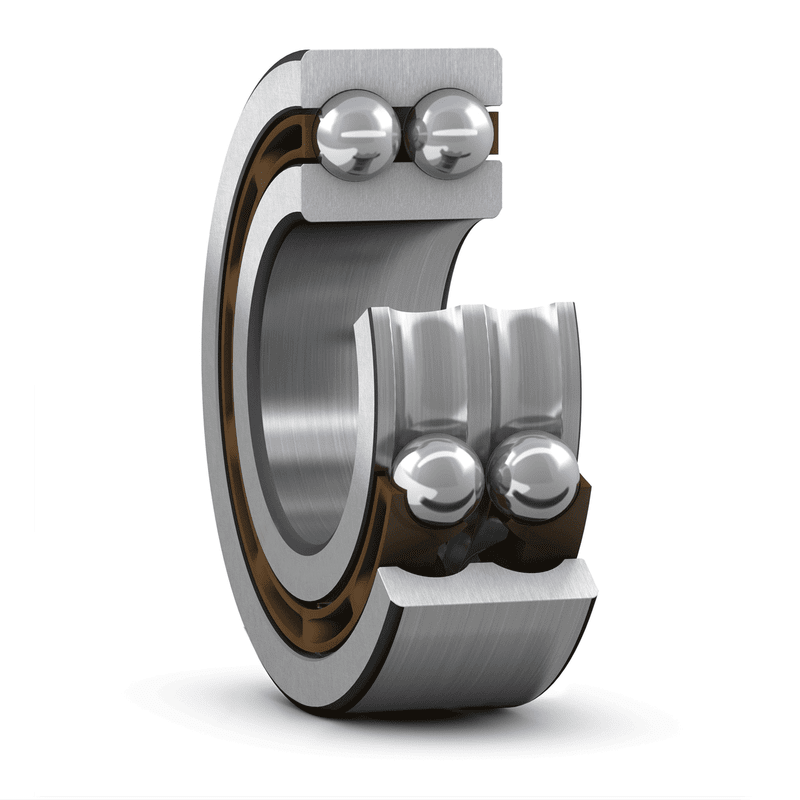

Double row deep groove ball bearings are very suitable for use in bearing configurations where the load-bearing capacity of single row deep groove bal...
 Copyright © 2002-2021 SKF Bearing Copyright Address:1-2F, Building 4, 1628 Lizheng Road, Lingang New Area, China (Shanghai) Pilot Free Trade Zone
Copyright © 2002-2021 SKF Bearing Copyright Address:1-2F, Building 4, 1628 Lizheng Road, Lingang New Area, China (Shanghai) Pilot Free Trade Zone