When choosing a match, the first thing to consider is the type of load that the collar can withstand. There are usually three types of loads that the ring can withstand:
1 Fixed load
The composite radial load acting on the ring is borne by the local area of the ring raceway and transmitted to the relative area of the shaft or bearing seat. This load is called a fixed load. The characteristic of fixed load is that the synthesized radial load vector is relatively stationary with respect to the collar. Both the ring and the composite radial load are fixed loads that do not rotate or rotate at the same speed. Loose fitting can be selected for the ring that can withstand fixed loads.
2 Rotating loads
The composite radial load acting on the ring, rotating along the circumference of the raceway and sequentially borne by various parts, is called rotational load.
The characteristic of rotational load is that the synthesized radial load vector rotates relative to the ring. There are three types of rotational loads:
(1) The direction of the load remains fixed and the collar rotates;
(2) The load vector rotates while the collar remains stationary;
(3) The load vector and the collar rotate at different speeds.
3 Swinging loads and indefinite loads
Sometimes the direction and magnitude of the load cannot be accurately determined, for example, in high-speed rotating machinery, in addition to the fixed direction load borne by the rotor weight, there is also a rotational load caused by unbalanced mass. If this rotational load is much larger than the fixed load, its composite load is still the rotational load; If the rotational load is much smaller than the fixed load, the composite load is the swinging load. Whether it is a rotating load or a swinging load, their magnitude and direction are constantly changing. In the variable working state, some rings may be subjected to rotating loads, fixed loads, and swinging loads. This type of load is called an indefinite load.
During the use of FAG bearings, improper operation, insufficient lubrication, rust and corrosion, as well as other factors such as current, external materials, eccentricity, etc., greatly reduce the service life of the bearings. Therefore, it is necessary to have sufficient knowledge and understanding of the preventive measures for bearings during the use of bearings.
A. External material of bearing:
Wear particle contamination and debris intrusion may cause wear, scratches, and dents on the bearing working surface. Preventive measures include removing invading particles and debris, replacing lubricants, and inspecting the sealing system
B. Improper operation of bearings:
Improper installation, operation, or disassembly of bearings may cause deformation or damage to the cage. Preventive measures include using appropriate tools for operation, installation, and disassembly, as well as using genuine Beijing Deruimei bearings.
C. Bearing eccentricity:
Eccentricity, tilt, or excessive load may lead to geometric stress concentration or surface peeling
The temperature of FAG bearings can generally be inferred from the temperature outside the bearing chamber. If the outer ring temperature of the bearing can be directly measured using oil holes, the bearing will be more suitable. Usually, the temperature of the bearing gradually increases as the bearing starts to operate and reaches a stable state after 1-2 hours. The normal temperature of bearings varies depending on the machine's heat capacity, heat dissipation, speed, and load. If the lubrication and installation parts are suitable, the bearing temperature will rise sharply, resulting in abnormal high temperatures. At this time, the operation must be stopped and necessary preventive measures must be taken.
Another lubrication method for bearings is oil mist lubrication, which is a form of micro lubrication that simply refers to using a small amount of lubricating oil to meet the lubrication requirements of rolling bearings. Oil mist lubrication is the process of turning lubricating oil into oil mist in an oil mist generator, and lubricating bearings through the oil mist. Due to the rolling of oil mist
D. Bearing current:
When the FAG bearing rotates and is energized, it may cause grooves or scratches to appear. When the bearing is stationary, improper electrical grounding during operation can cause minor burns. Preventive measures include reducing or avoiding current flow through the bearing through appropriate grounding connections before welding components other than the bearing
E. Insufficient lubrication of bearings:
Insufficient or improper lubricating oil may lead to component scratches or severe deformation of FAG bearings. Preventive measures: improve the lubrication system and regularly replenish or replace lubricants appropriately
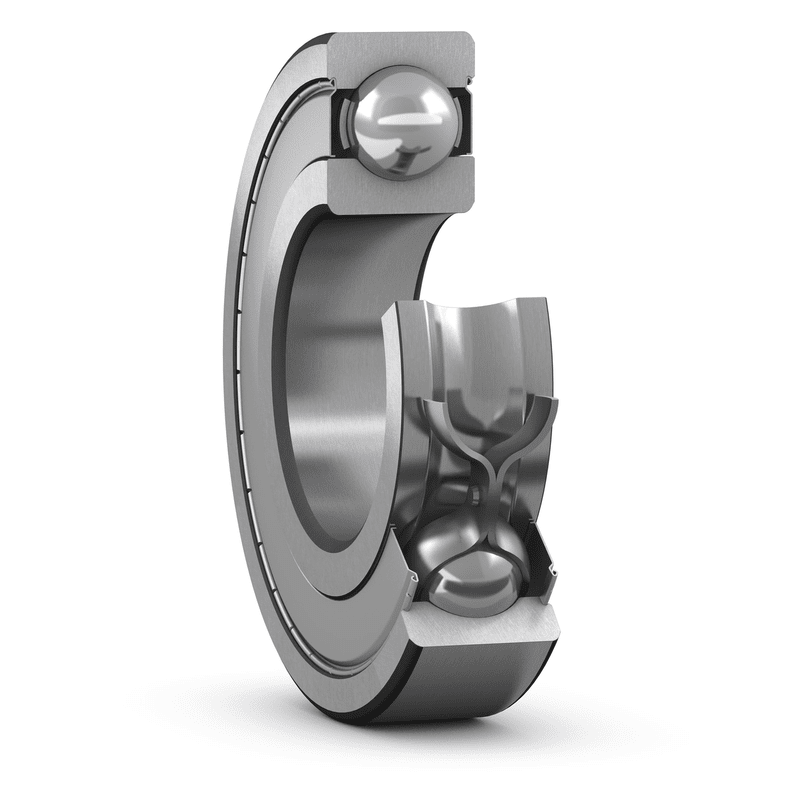

Single row deep groove ball bearings are the most widely used type of bearing. Provide closed (with sealed or dust cover) or open design. Open type be...
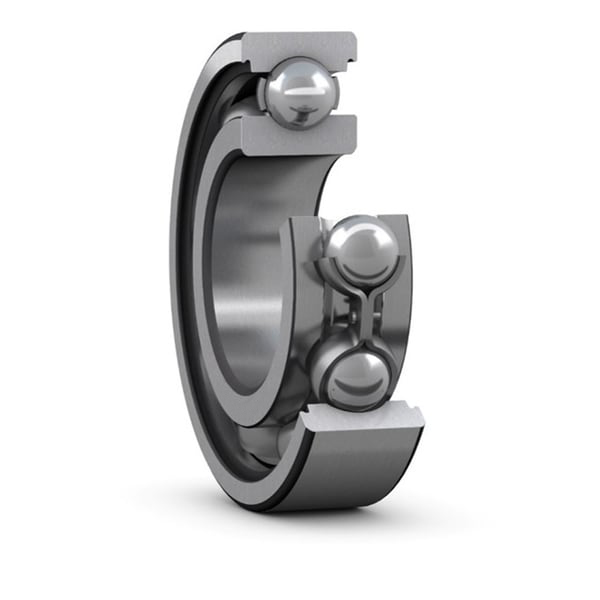

Stainless steel deep groove ball bearings can resist corrosion caused by moisture and other media. Provide closed (with sealed or dust cover) or open ...
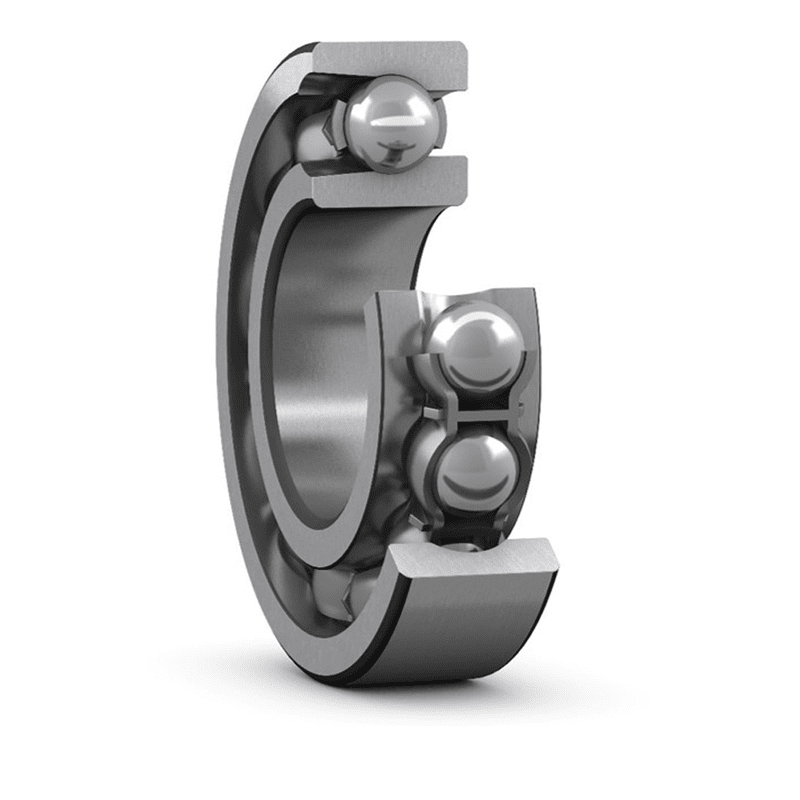

A single row deep groove ball bearing with a ball loading notch has a ball loading notch on both the inner and outer rings, which is used to load more...
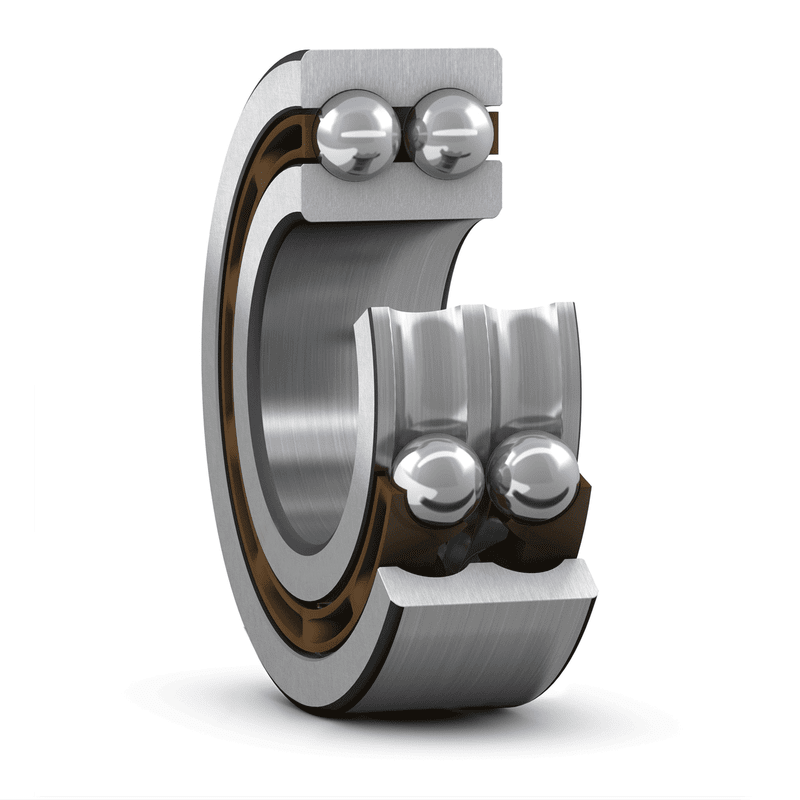

Double row deep groove ball bearings are very suitable for use in bearing configurations where the load-bearing capacity of single row deep groove bal...
 Copyright © 2002-2021 SKF Bearing Copyright Address:1-2F, Building 4, 1628 Lizheng Road, Lingang New Area, China (Shanghai) Pilot Free Trade Zone
Copyright © 2002-2021 SKF Bearing Copyright Address:1-2F, Building 4, 1628 Lizheng Road, Lingang New Area, China (Shanghai) Pilot Free Trade Zone