The increasingly stringent market requirements for imported bearings include equipment and other attributes, as well as diverse performance. To select suitable bearings from a large number of structures and sizes, different angles are required. When choosing a bearing, it is generally believed that the difficulty of installation and removal, bearing size, market availability, and other factors that allow for space generally determine the bearing structure. Comparative study on the design lifespan of various machinery and the limitations of durable bearings, while determining the bearing size. When choosing imported bearings, bearings often tend to believe that the grease life, fatigue life, wear resistance, low noise, and other factors that occur during aging also need to be fully studied.
In addition, according to different applications, it is necessary to choose specially designed bearings with requirements for accuracy, clearance, cage structure, lubricating grease, and other aspects. However, there is no specific order or rule for selecting bearings. Priority should be given to the conditions, performance, and related matters required by the bearings, especially practicality. As long as the bearings are kept in good original performance as much as possible, maintenance and upkeep should be prioritized to prevent accidents, ensure operational reliability, improve productivity and economy. Corresponding mechanical operation and maintenance standards, regular, and good conditions. This includes monitoring the operating status, replenishing or replacing lubricants, and regularly checking and cleaning. As a maintenance operation issue, there are issues such as bearing rotation noise, vibration, temperature, lubrication conditions, etc.
Bearing cleaning: Remove the bearing for repair, record the appearance of the bearing for the first time, confirm the remaining amount of lubricant, sample and inspect the lubricant used, and clean the bearing. As cleaning agents, gasoline and kerosene are generally used. Remove the bearing for cleaning, cleaning, and fine cleaning, place it in a container, and place the first metal mesh bottom in a container that does not directly contact the dirt on the bearing. Rough cleaning, if the bearing rotates and becomes dirty, damaging the rolling surface of the bearing, attention should be paid. In crude oil cleaning, use a brush to remove grease and viscous materials, generally clean, and wash until fine. Fine cleaning is to wash the oil while the bearing rotates on one side and carefully clean it on the other side. In addition, the cleaning oil must be kept clean.
Maintenance and judgment of bearings: It is necessary to determine whether they can be used for cleaning and disassembling bearings. Check the raceway, raceway, surface condition, cage wear, bearing clearance, and improvement of dimensional accuracy for any unrelated damage or abnormalities. Non separable small ball bearing, inner ring, supported horizontally with one hand, rotate outer ring to confirm smooth operation. Conical roller bearings and equally spaced bearings can roll the body, and the outer raceway surface has been inspected. Large bearings, as they cannot be rotated by hand, require careful inspection of the raceway, cage, and walls of the rolling elements, such as appearance. The importance of higher bearings requires more careful inspection.
A comprehensive technology that judges and predicts the reliability and performance of bearings based on their faults and degradation, performance status parameters, identifies and judges the location, cause, and degree of danger of abnormal situations, and determines repair and improvement methods. Therefore, the fault diagnosis technology of bearings is not simply a fault detection (or monitoring) technology, nor is it simply a point inspection instrumentation. Accurately, quickly, and effectively collect signals, process data, manually or automatically identify and judge. In order to determine the scientific repair cycle, necessary tests and estimates of fatigue and wear life should also be conducted based on the mechanisms of various faults.
The reason for fatigue failure is that fatigue failure is one of the common failure forms on the surface of various bearings, which is caused by the long-term action of alternating loads on metals, mainly manifested as the initiation, propagation, and fracture of fatigue cracks.
There are two ways in which cracks can occur:
Cracks originate from the surface layer, that is, under the repeated action of surface contact stress, crack Z initially occurs at a certain depth from the contact surface and develops in a direction at a certain angle to the surface. After reaching a certain depth from the surface, it extends beyond the surface and forms pitting and peeling, leaving behind pits on the contact surface.
As mentioned earlier, the smelting quality of materials is largely related to the quality of material smelting, including pitting corrosion failure and fatigue failure. Surface defects, looseness, and slag inclusion are the root causes of pitting corrosion and the main parts of fatigue failure. Research has shown that the impact of non-metallic inclusions on bearing life varies with the type, shape, and quantity of inclusions, with spherical non deformable inclusions posing a serious threat to bearing life.
The surface machining accuracy of parts affects the distribution of contact stress. The worse the surface processing accuracy, the more severe the load concentration in the surface contact area, the greater the contact stress, and the more prone to fatigue failure. The smaller the surface roughness Ra value, the lower the stress concentration, and the higher the contact fatigue life. Research has shown that increasing the surface roughness from Ra=0.4mm to Ra=0.1mm can increase the contact fatigue life by 6-8 times.
The selection and fixing method of sensors depend on the structural characteristics of the bearing and different usage conditions. The vibration caused by it may be low-frequency pulsation with a frequency of about 1kHz or below (through vibration), or high-frequency vibration with a frequency of 1kHz or above, thousands or even tens of kilohertz (inherent vibration), usually containing both types of vibration components. Therefore, when detecting the vibration velocity and acceleration signals of bearings, both frequency bands should be covered simultaneously or separately. If necessary, filters can be used to extract the required frequency components.
A high pass filter with a cut-off frequency of 1kHz is used to filter out low-frequency components below 1kHz to eliminate mechanical interference; Then use the peak value, RMS value, or kurtosis coefficient of the signal as monitoring parameters. Many simple bearing monitoring instruments and meters use this method
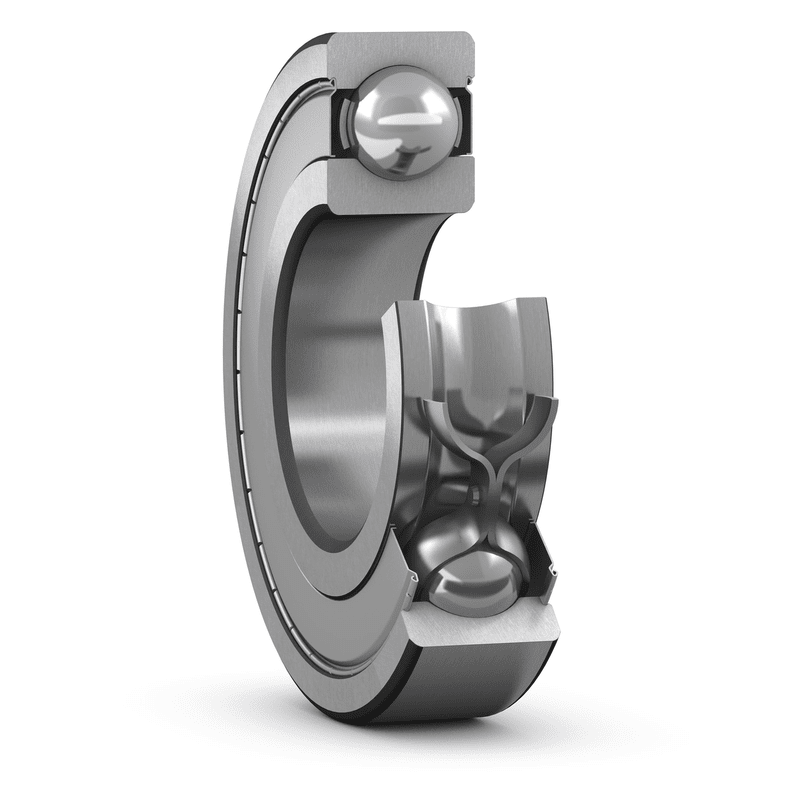

Single row deep groove ball bearings are the most widely used type of bearing. Provide closed (with sealed or dust cover) or open design. Open type be...
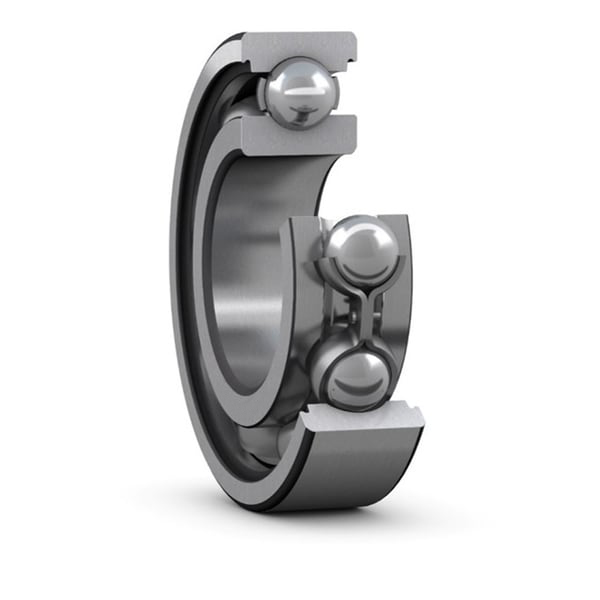

Stainless steel deep groove ball bearings can resist corrosion caused by moisture and other media. Provide closed (with sealed or dust cover) or open ...
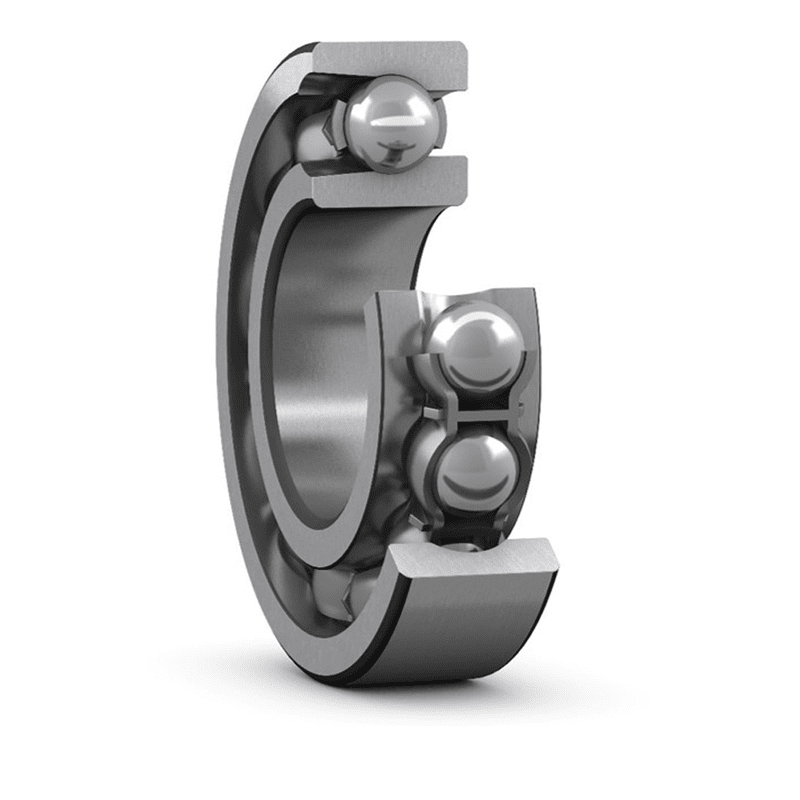

A single row deep groove ball bearing with a ball loading notch has a ball loading notch on both the inner and outer rings, which is used to load more...
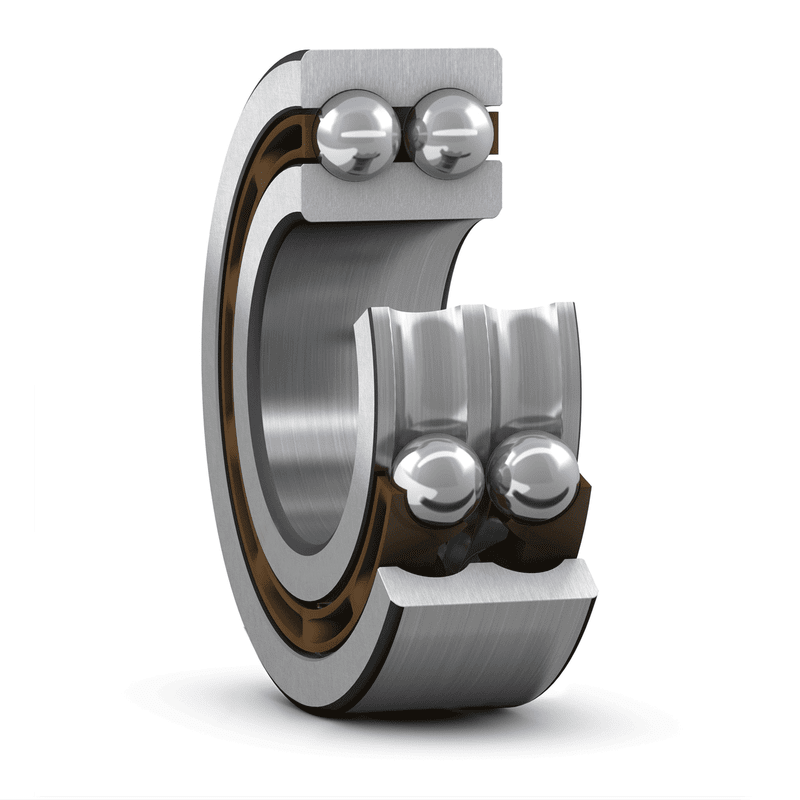

Double row deep groove ball bearings are very suitable for use in bearing configurations where the load-bearing capacity of single row deep groove bal...
 Copyright © 2002-2021 SKF Bearing Copyright Address:1-2F, Building 4, 1628 Lizheng Road, Lingang New Area, China (Shanghai) Pilot Free Trade Zone
Copyright © 2002-2021 SKF Bearing Copyright Address:1-2F, Building 4, 1628 Lizheng Road, Lingang New Area, China (Shanghai) Pilot Free Trade Zone